
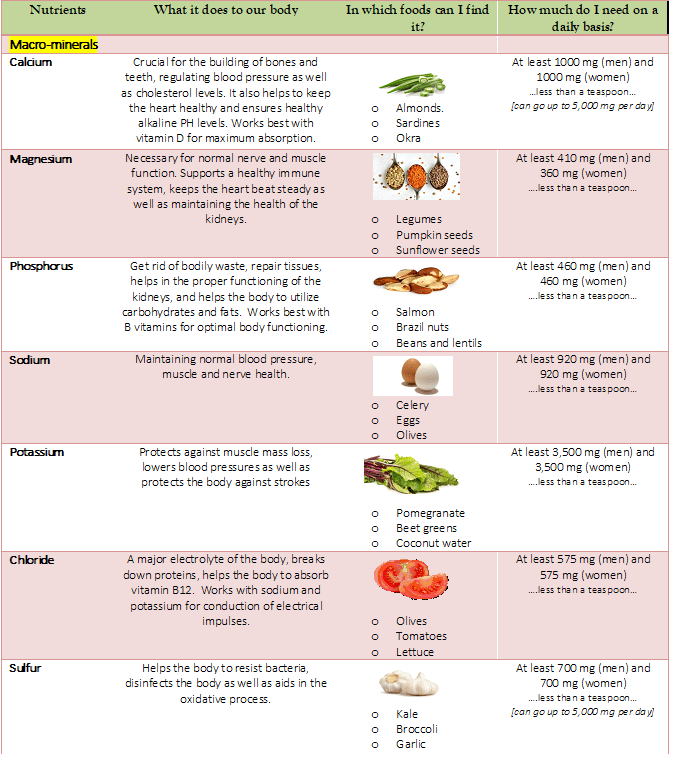
I have gained profound experiences in public health sector under different thematic areas of health, nutrition, sexual and reproductive health, maternal and newborn health, research etc., targeting diverse audience of different age groups. Grant School of Public Health, Bangladesh. Hello and greetings everyone! I am Kusum Wagle, MPH, WHO-TDR Scholar, BRAC James P. From polyunsaturated fats: 10% of total energy.From monounsaturated fats: 20% of total energy.From protein: 15-20% of total energy or 1g/kg body weight per day.From carbohydrates: 55–75% of total energy.Overdose of micro-nutrients may harm specific organs of the body. Overdose of macro-nutrients causes obesity, heart diseases, diabetes and other metabolic syndromes Micro-nutrients are toxic if present exorbitantly in the cell than the required amount.Įxcessive intake of micro-nutrients leads to obesity and diabetes.Įxcessive consumption of micro-nutrients leads to suppressing immune function.ĭeficiency of macro-nutrients causes Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM), Kwashiorkor, marasmus etc.ĭeficiency of micro-nutrients causes different diseases like night blindness, beriberi, scurvy, goiter etc. Macro-nutrients are normally not toxic to the cell if they are present in comparatively higher concentration than in the normal level. Micro-nutrients include zinc, iron, manganese, copper, boron, molybdenum and chlorine in trace quantities. Secondary macro-nutrients include calcium, magnesium, and sulfur in lesser quantity.

Primary macro-nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in larger quantities. Micro-nutrients are not classified in different types, as it is required in trace amount. Macro-nutrients are divided into two classes: Primary and Secondary, as they are required in large quantities. Examples: iron, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus, zinc etc. There are mainly three macro-nutrients required by the body carbohydrate, protein and fatsĭifferent types of micro-nutrients required by the body include vitamins, minerals and trace elements. Mainly vegetables, fruits, eggs, green leafy vegetables, fermented foods are rich in micro-nutrients. Micro-nutrients are also called trace elements.Ĭereals, legumes, meat, fish, yams, potatoes, nuts, oilseeds are rich in macro-nutrients. Macro-nutrients are also called as major elements. Micro-nutrients are present in minute concentration inside the body. Macro-nutrients are available in high concentration inside the body. Micro-nutrients do not have any role in the construction of body composition. Macro-nutrients plays a vital role in the construction of body composition.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
